Lesson 8: Minerals – Calcium , Phosphorus and Magnesium
8.2 Enteral nutrition requirements
Mineral supplementation is not straightforward, even if a target intake has been identified. Human milk fortifiers or preterm formulas are designed to add sufficient minerals to the preterm diet, but intake may not lead to accretion if these minerals are not well absorbed in the intestine. Vitamin D levels can affect absorption as can the ratio of Ca and P in the supplement (Mimouni et al. 2014).
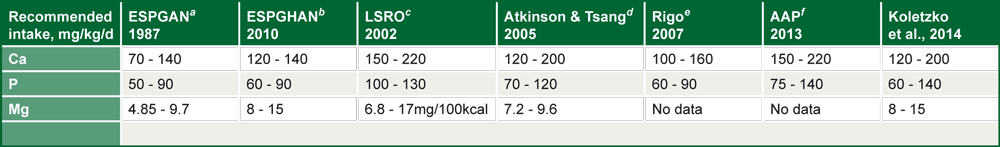
The recommended mineral intakes from different expert groups are summarized in table 5.
Table 5: Recommendations from different expert groups for daily enteral intake of Ca, P and Mg for preterm VLBW infants (up to 40 weeks of postnatal age)
Adapted from: Mimouni et al. 2014.
a) ESPGAN=European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition (ESPGAN 1987);
b) ESPGHAN=European Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition Committee (Agostoni et al. 2010);
c)LSRO=Life Science Research Office (Klein 2002);
f) AAP=American Academy of Pediatrics (Abrams & Committee on Nutrition 2013).